Population Standard Deviation Calculator
Calculate population standard deviation (σ) with detailed results and visual graph
Population Standard Deviation Graph
Step-by-Step Solution
The dataset entered: 41, 35, 55, 56, 57
Count of numbers (N): 5
Mean (μ) = Sum of all values / Count of values
μ = (41 + 35 + 55 + 56 + 57) / 5 = 244 / 5 = 48.8
Mean: 48.8
For each value, subtract the mean and square the result:
| Value (x) | Deviation (x – μ) | Squared Deviation (x – μ)² |
|---|---|---|
| 41 | -7.8 | 60.84 |
| 35 | -13.8 | 190.44 |
| 55 | 6.2 | 38.44 |
| 56 | 7.2 | 51.84 |
| 57 | 8.2 | 67.24 |
| Sum | – | 408.8 |
For population: Variance (σ²) = Sum of squared deviations / N
σ² = 408.8 / 5 = 81.76
Population Variance: 81.76
Population Standard Deviation (σ) = √Variance
σ = √81.76 ≈ 9.0421
Population Standard Deviation: 9.0421
In the world of statistics, the population standard deviation is one of the key metrics used to measure the variability or spread of data. It helps in understanding how much the data points in a dataset deviate from the mean, providing valuable insights for decision-making in a variety of fields. The population standard deviation calculator is an indispensable tool that allows users to quickly calculate this important statistical value without having to compute complex formulas manually. This article examines the concept of population standard deviation, its calculation, and the practical applications of a population standard deviation calculator across various sectors.
What is Population Standard Deviation?
Before diving into the calculator itself, it’s important to understand what population standard deviation is and how it differs from other related concepts. In simple terms, the population standard deviation is a measure of how much each individual value in a dataset deviates from the population mean (average). It gives a sense of how spread out the data points are in relation to the average value.
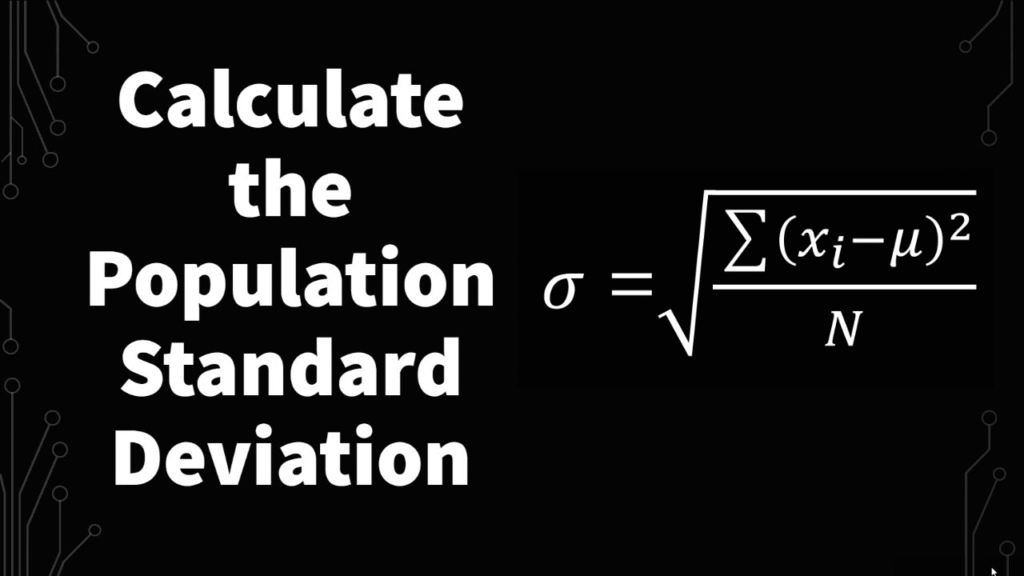
The formula for population standard deviation is as follows:
σ=∑i=1N(xi−μ)2N\sigma = \sqrt{\frac{\sum_{i=1}^{N} (x_i – \mu)^2}{N}}σ=N∑i=1N(xi−μ)2
Where:
- σ\sigmaσ is the population standard deviation
- NNN is the total number of data points in the population
- xix_ixi represents each data point
- μ\muμ is the mean (average) of the data points
- ∑\sum∑ is the sum of squared deviations from the mean.
This formula is applied when you have access to the entire population of data points, unlike the sample standard deviation formula, which is used when dealing with a subset of the population.
Key Differences Between Population and Sample Standard Deviation
While both population standard deviation and sample standard deviation measure the spread of data, they differ slightly in their calculation. The main difference lies in the denominator used in the formula. When calculating the population standard deviation, the denominator is NNN, the total number of data points in the population. However, for the sample standard deviation, the denominator is n−1n-1n−1, where nnn is the number of sample points. This adjustment in the formula helps to correct the bias that may occur when using a sample to estimate a population parameter.
How a Population Standard Deviation Calculator Works
Calculating the population standard deviation manually can be cumbersome, especially when dealing with large datasets. A population standard deviation calculator simplifies this process by automating the calculation. The user simply inputs the dataset, and the calculator handles the rest. Here is an overview of how the population standard deviation calculator works:
- Input the Data: Enter the complete dataset into the calculator. This could be a list of numbers or values that represent the population you are studying.
- Calculate the Mean: The calculator will automatically compute the mean (average) of the dataset by adding up all the values and dividing by the total number of data points.
- Subtract the Mean from Each Data Point: For each data point, the calculator will subtract the mean to find the deviation from the mean.
- Square Each Deviation: The calculator will then square each of these deviations to eliminate negative values and emphasize larger deviations.
- Sum of Squared Deviations: Next, the calculator will sum all the squared deviations from step 4.
- Divide by the Total Number of Data Points: The calculator will divide the sum of squared deviations by the total number of data points in the population (N).
- Calculate the Square Root: Finally, the calculator will take the square root of the result to give the population standard deviation.
This step-by-step automation allows users to obtain accurate results quickly and with minimal effort.
Applications of Population Standard Deviation
The population standard deviation is widely used across various fields. Here are some of the key areas where it plays a crucial role:
1. Finance and Investment Analysis
In finance, standard deviation is used to measure the risk or volatility of an investment portfolio. A higher standard deviation indicates that the investment is more volatile, with returns varying greatly over time. Conversely, a lower standard deviation suggests a stable, less risky investment. By calculating the population standard deviation of historical returns, investors can assess the risk level of different investment options and make more informed decisions.
2. Healthcare and Medicine
In healthcare, population standard deviation is used to measure the variation in medical data. For example, doctors may use it to understand the variation in blood pressure readings or test results across a population of patients. By examining the population standard deviation, healthcare professionals can identify outliers and assess the effectiveness of treatments or interventions.
3. Education and Testing
In educational assessments, population standard deviation is often used to measure the spread of test scores. If a test has a high standard deviation, it indicates that the scores are widely spread out, suggesting that there is significant variation in student performance. Conversely, a low standard deviation implies that most students performed similarly.
4. Social Welfare Programs
In the context of social welfare programs or poverty alleviation schemes, the population standard deviation can be used to measure the variation in income levels, health outcomes, or educational achievements across different regions. If a region has a high standard deviation in income, it might suggest significant economic disparities that require targeted interventions.
5. Manufacturing and Quality Control
In the manufacturing industry, population standard deviation is used to measure the consistency of product quality. By calculating the population standard deviation of product measurements (e.g., length, weight, or tolerance), manufacturers can ensure that their products meet quality standards and are within acceptable specifications.
Benefits of Using a Population Standard Deviation Calculator
Using a population standard deviation calculator offers several benefits, particularly when working with large datasets. These include:
1. Speed and Efficiency
Manual calculations of standard deviation can be time-consuming, especially for large datasets. The population standard deviation calculator automates the process, providing results in seconds and freeing up time for analysis and decision-making.
2. Accuracy
When performing manual calculations, there is always the risk of making mistakes, especially when dealing with large numbers. The population standard deviation calculator ensures that the calculations are accurate and free from human error.
3. Ease of Use
A population standard deviation calculator is user-friendly and does not require advanced mathematical knowledge. This makes it accessible to people from all backgrounds, including students, researchers, and professionals.
4. Scalability
Calculating standard deviation for large datasets manually can become overwhelming. With a population standard deviation calculator, you can handle datasets of any size, ensuring that your calculations are quick and accurate regardless of the amount of data.
5. Cost-Effectiveness
Most population standard deviation calculators are available for free or at a low cost, making them an affordable option for individuals, organizations, and businesses who need to perform statistical analyses regularly.
Real-World Examples of Population Standard Deviation
To understand the practical application of population standard deviation, let’s consider a few real-world examples:
Example 1: Investment Portfolio Analysis
Imagine you have a portfolio of stocks and you want to calculate the population standard deviation of their monthly returns over the past year. By inputting the monthly return data into a population standard deviation calculator, you can easily determine the volatility of your portfolio. If the standard deviation is high, you may decide to rebalance your portfolio to reduce risk.
Example 2: Health Outcomes in a Study
In a medical study, researchers may be examining the blood pressure levels of a group of 100 patients. By calculating the population standard deviation of their readings, they can assess the variation in blood pressure across the group. A high standard deviation may suggest that there are outliers (e.g., patients with exceptionally high or low blood pressure), which may require further investigation.
Example 3: Testing and Exam Scores
In an educational setting, a teacher may want to analyze the variation in exam scores among students. By calculating the population standard deviation of the scores, the teacher can gauge how well students are performing relative to each other. If the standard deviation is large, it may indicate that some students are struggling significantly, prompting the teacher to adjust the teaching approach.
Challenges of Using Population Standard Deviation
While population standard deviation is an invaluable statistical tool, it does have its limitations:
1. Sensitivity to Outliers
Population standard deviation is sensitive to extreme values or outliers in the dataset. A few unusually high or low values can significantly skew the results, making the data appear more variable than it actually is.
2. Assumption of Normality
The formula for population standard deviation assumes that the data follows a normal (bell-shaped) distribution. If the data is highly skewed or not normally distributed, the standard deviation may not provide an accurate representation of the spread of the data.
3. Interpretation Challenges
While the standard deviation is useful, it may not always provide a clear picture of data distribution, especially if the data is heavily skewed. In such cases, other measures like the interquartile range (IQR) or median absolute deviation (MAD) may be more appropriate.
Future Prospects of Population Standard Deviation Calculators
With the increasing availability of advanced statistical software and online tools, the future of population standard deviation calculators looks promising. These tools will continue to evolve, offering more features such as:
- Real-time data processing for instant results
- Visualization options such as graphs and charts to better understand data distribution
- Integration with other statistical functions for comprehensive data analysis
- Cloud-based platforms that allow easy sharing and collaboration on data analysis
As technology advances, we can expect population standard deviation calculators to become even more efficient, accurate, and user-friendly.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between population standard deviation and sample standard deviation?
The population standard deviation is used when you have data from the entire population, while the sample standard deviation is used when you have data from a subset of the population. The key difference is in the denominator of the formula: NNN for the population and n−1n-1n−1 for the sample. - Can I use a population standard deviation calculator for sample data?
While you can technically use a population standard deviation calculator for sample data, it’s important to adjust the formula for sample standard deviation by dividing by n−1n-1n−1 instead of NNN. For accuracy, use a sample standard deviation calculator for sample data. - How do I interpret the result of a population standard deviation calculation?
A larger population standard deviation indicates more variability in the data, while a smaller value suggests that the data points are closely clustered around the mean. - Is a high standard deviation always bad?
Not necessarily. A high standard deviation can indicate greater diversity or variability, which can be desirable in some contexts (e.g., in investment returns). However, in other cases (e.g., manufacturing), it could suggest inconsistency or a lack of quality control. - Can a population standard deviation calculator handle large datasets?
Yes, population standard deviation calculators are designed to handle datasets of any size. They are especially useful when dealing with large datasets that would be cumbersome to analyze manually. - How accurate is the population standard deviation calculator?
As long as the data input is correct, the population standard deviation calculator provides highly accurate results by following the standard formula. - What other statistical measures can I calculate using an online calculator?
Many online calculators can compute other statistical measures such as mean, median, variance, range, and more, making them comprehensive tools for data analysis.
Conclusion
The population standard deviation calculator is an essential tool in the world of data analysis. It simplifies the process of calculating variability within a population and offers numerous benefits in fields such as finance, healthcare, education, and manufacturing. By understanding the significance of population standard deviation and utilizing calculators effectively, individuals and organizations can make more informed decisions, reduce risk, and optimize their operations. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or professional, incorporating population standard deviation into your data analysis toolkit will undoubtedly enhance your ability to interpret data and draw meaningful conclusions.
